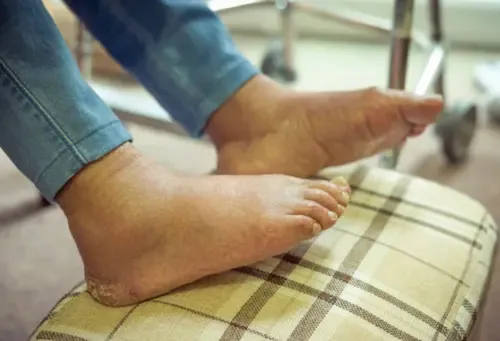
Edema, characterized by the swelling of body tissues, particularly in the lower legs and feet, is a prevalent condition that affects many individuals. While medication can provide temporary relief, it is crucial to address the underlying causes to effectively manage and prevent edema. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various factors that contribute to edema, along with practical solutions to alleviate the condition.
Sugar and a High Carb Diet: The Double-Edged Sword
Consuming excessive amounts of sugar and maintaining a high-carbohydrate diet can significantly contribute to the development of edema. When we consume sugar, our body stores it as glycogen, a compound comprised of glucose molecules bound together with potassium. For every glucose molecule stored, three water molecules are retained, resulting in significant water retention and subsequent swelling. Moreover, excessive sugar consumption depletes the body's potassium levels, further exacerbating fluid retention. To combat edema caused by sugar and refined carbs, adopting a low-carb diet, such as the ketogenic diet, can prove beneficial.
Sodium and Potassium Imbalance: Finding the Right Balance
An imbalance between sodium and potassium levels in the body can lead to fluid retention and edema. While sodium is known to retain fluid, potassium serves as an antidote, helping to maintain balance. However, consuming excessive amounts of sodium without adequate potassium intake can result in fluid retention. Many individuals fall short of the recommended daily potassium intake, which stands at 4,700 milligrams. Increasing potassium-rich foods in the diet, such as green leafy vegetables, or supplementing with potassium electrolytes, can help restore the sodium-potassium balance and alleviate edema.
Medication Side Effects: A Common Culprit
Certain medications can cause edema as a side effect. If you notice swelling in your lower legs after starting a new medication, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to explore alternative options or adjust the dosage. Common medications associated with edema include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), calcium channel blockers, diabetic medications, and steroids. Additionally, it is essential to support liver health when taking medications, as the liver is often the organ most affected. Milk thistle, a natural liver protective remedy, can help mitigate potential complications.
Protein Deficiency and Organ Damage: A Deeper Connection
Low protein levels in the blood can contribute to edema, primarily when stemming from liver or kidney damage. The liver produces essential proteins like albumin, which helps retain water within the bloodstream. Liver conditions, such as cirrhosis or a fatty liver, can impair protein production, leading to fluid accumulation in the tissues. Similarly, kidney damage can result in protein loss through urine, further exacerbating fluid retention. Addressing the underlying liver or kidney condition is crucial to managing edema caused by protein deficiency.
Heart Conditions and Edema: A Direct Link
Heart problems, including congestive heart failure, can directly contribute to the development of edema. When the heart fails to pump blood efficiently, fluid can accumulate in the capillaries, leading to swelling in the lower extremities. High blood pressure can also push fluid into the tissues, causing edema. Managing and treating the underlying heart condition is essential to alleviate edema. Consult with your healthcare provider to explore natural remedies and lifestyle modifications that support heart health.
Thyroid Dysfunction and Mixed Edema: An Unusual Connection
Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can contribute to mixed edema, a condition characterized by abnormal fat accumulation in the lower body. Estrogen receptors play a role in this hormonal and genetic condition, leading to fat accumulation primarily in the lower body. Pregnancy, puberty, and menopause can trigger this condition due to hormonal imbalances. Treating the underlying thyroid dysfunction and adopting a low-carb, higher-fat diet may help manage mixed edema.
Lymphedema: A Complex Challenge
Lymphedema is a challenging condition characterized by congestion and accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues. The lymphatic system, responsible for fluid drainage, may experience backup and congestion, leading to edema. Manual lymphatic drainage, compression garments, low-level laser therapy, and regular exercise have shown promise in managing lymphedema. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a tailored treatment plan.
Other Factors and Additional Considerations
In addition to the aforementioned causes, certain factors can contribute to edema. These include the side effects of medications, such as diuretics, which can result in potassium depletion. Additionally, lipedema, a condition associated with abnormal fat accumulation, particularly in the lower body, may contribute to edema. While lipedema is challenging to treat, adopting a low-carb, higher-fat diet has shown positive results in some cases.
Conclusion
Edema, characterized by swelling in the lower legs and feet, can be caused by various factors ranging from dietary choices to organ damage. Addressing the underlying causes is crucial for effective management and prevention. By adopting lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a low-carb diet, balancing sodium and potassium intake, and seeking appropriate medical guidance, individuals can alleviate the symptoms of edema and improve their overall well-being. Remember, consulting with healthcare professionals is essential to develop a personalized approach for managing edema effectively.