Diabetes is a complex metabolic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. While most people are aware of the impact of diabetes on blood sugar levels and overall health, many may not realize that this condition also has a profound effect on the skin. Our skin can provide valuable insights into our internal health, and certain skin problems can be indicators of diabetes. In this article, we will explore the relationship between diabetes and various skin conditions, as well as discuss the importance of managing blood sugar levels for overall skin health.
Understanding Insulin and Its Role in Skin Health
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. In individuals with diabetes, either the body does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or does not effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). This disruption in insulin function can have a significant impact on the skin.
Acanthosis Nigricans: A Sign of Insulin Resistance
One of the common skin conditions associated with insulin resistance, a precursor to Type 2 diabetes, is acanthosis nigricans. This condition is characterized by darkening and thickening of the skin, particularly in areas with folds such as the armpits, neck, and elbows. Insulin resistance leads to an overproduction of skin cells called melanocytes, which produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. As a result, individuals with insulin resistance may notice darkened and velvety patches of skin in these areas.
Skin Tags: An Indicator of Elevated Insulin
Insulin, being an anabolic hormone, promotes growth. When insulin levels are elevated, such as in individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance, it can lead to the growth of benign skin growths known as skin tags. These small, harmless growths can appear in various parts of the body and are often a visible sign of increased insulin levels.
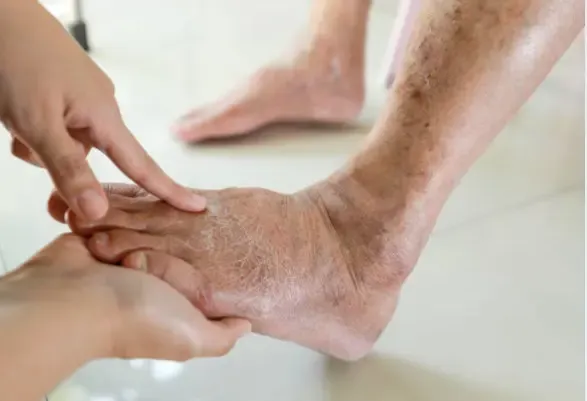
Digital Sclerosis: Thickened Skin and Insulin
Elevated insulin levels can also affect the texture and thickness of the skin, leading to a condition known as digital sclerosis. This skin condition is characterized by rough, thickened skin with a dry and flaky appearance. Insulin influences the growth of skin cells called keratinocytes, causing them to grow abnormally and resulting in thicker and rougher skin.
Acne and Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, particularly common in conditions like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), can lead to increased levels of androgen hormones. These hormones can affect the sebaceous glands in the skin, leading to an increased risk of acne breakouts. The relationship between elevated insulin and androgen levels underscores the importance of managing blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes to reduce the risk of skin problems like acne.
Impaired Immune System and Skin Infections
High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. Certain bacterial infections can lead to the formation of cysts, such as Baker cysts. Interestingly, there is a notable correlation between individuals with diabetes and the presence of Baker cysts, highlighting the connection between blood sugar regulation, immune function, and skin health.
Blood Sugar Levels and Skin Circulation
Diabetes can have profound effects on the circulation of blood to the skin, particularly in the lower extremities. When blood sugar levels remain high, the tiny capillaries responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the skin can be damaged. This can result in the appearance of small red or purple dots known as petechiae or larger blotches called purpura. These skin discolorations occur due to the leaking of blood from damaged capillaries into the surrounding tissues.
Gangrene: A Severe Complication of Diabetes
In severe cases of diabetes where blood circulation is significantly compromised, a condition called gangrene can develop. Gangrene is characterized by the death of tissue, often leading to discoloration of the affected areas, such as the feet and toes. The lack of blood flow and oxygen to the tissues can cause them to turn green, black, brown, or blue. Gangrene can be a severe complication of diabetes and may ultimately require amputation to prevent the spread of infection.
Leg Ulcers: Poor Circulation and Infection
Poor circulation associated with diabetes can also lead to the development of leg ulcers. These painful sores often occur in areas where blood flow is compromised, such as the feet. The combination of impaired circulation and a weakened immune system makes individuals with diabetes more susceptible to infections, further complicating the healing process.
Puffy and Swollen Eyelids: A Telltale Sign
The impact of diabetes on the skin is not limited to the lower extremities. In individuals with uncontrolled diabetes, fluid retention can manifest as puffy and swollen eyelids. This visible sign is a result of the excess fluid accumulating in the soft tissues around the eyes. While puffy eyelids can be a symptom of various conditions, it is important to recognize that diabetes can contribute to this particular manifestation.
Managing Diabetes for Improved Skin Health
While various skin conditions can indicate diabetes, it is crucial to address the underlying cause by effectively managing blood sugar levels. Medications are commonly prescribed to help regulate blood sugar, but it is equally important to adopt lifestyle changes that promote overall skin health.
A Low-Carb Diet: Balancing Blood Sugar
A low-carb diet can be highly beneficial for individuals with diabetes. By reducing the intake of carbohydrates, blood sugar levels can be better controlled, leading to improved insulin sensitivity. Incorporating healthy fats, proteins, and fiber-rich foods into the diet can help stabilize blood sugar and minimize the risk of skin-related complications.
Intermittent Fasting: Enhancing Insulin Sensitivity
Intermittent fasting is another strategy that has shown promise in managing blood sugar levels and enhancing insulin sensitivity. By restricting the eating window and allowing for periods of fasting, the body becomes more efficient at utilizing insulin and maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Intermittent fasting can be tailored to individual preferences and schedules, making it a flexible approach to diabetes management.
Apple Cider Vinegar: A Natural Aid
Apple cider vinegar has gained popularity for its potential benefits in blood sugar management. Consuming a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar diluted in water several times a day has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and aid in the regulation of blood sugar levels. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating apple cider vinegar into your routine, as individual responses may vary.
Berberine: A Natural Alternative to Medication
Berberine, a natural compound found in certain plants, has been extensively studied for its potential in managing blood sugar levels. Research has shown that berberine has comparable effects to the diabetes medication Metformin in regulating blood sugar and improving insulin sensitivity, without the associated side effects. Incorporating berberine into your diabetes management plan may offer additional support for skin health.
Conclusion
The skin serves as a window into our overall health, and the presence of certain skin conditions can indicate underlying diabetes or insulin resistance. Understanding the connection between diabetes and skin health is essential for effective management and prevention of complications. By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, such as a low-carb diet and intermittent fasting, along with natural aids like apple cider vinegar and berberine, individuals with diabetes can improve their skin health and overall well-being. Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance in managing diabetes and its associated skin conditions.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is not intended as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment options.